- Related articles
- Applicable to 10GBASE-LRL Standard Optical Transceiver Models
- The Difference between SFP+ and X2
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco SG200-50FP-EU Switch
- Optical Transceivers for WS-C4948E Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C3650-48PS-L Switch
- The Things You Need to Know about 1000BASE-FX Ethernet Standards
- All Cisco DS-SFP-GE-T's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility matri
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960X-48LPS-L Switch
- Optical Transceivers for Cisco WS-C2960S-48TS-L Switch
- Bi-Directional QSFP — 40GbE Over LC Duplex Multimode Fiber

Introduction
In this article we will discuss about the 10GBASE-T Ethernet standard and what are the difference between 10GBASE-T and 1000BASE-T, So you can have a basic understanding for 10GBASE-T technology to understand the basic solutions to 10GBASE-T. products.
What is the 10GBASE-T technology?
10GBASE-T adoption has been fueled by a wide ecosystem of adapter/switches vendors coinciding with the release of the 40nm 10GBASE-T PHY in 2012 with new innovations, cost points and technology maturity driving large deployment. 10GBASE-T applications have symmetrical data flow. The nature of EEE in 10GBASE-T is that it applies independently in each direction. So a link with high traffic in one direction, and light traffic in the opposite direction can leverage EEE to minimize overall power.
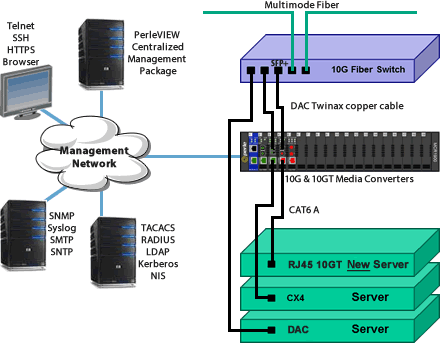
What are the Difference Between 10GBASE-T and 1000BASE-T?
10GBASE-T, or IEEE 802.3an-2006, is a standard released in 2006 to provide 10 Gbit/s connections over unshielded or shielded twisted pair cables, over distances up to 100 meters (330 ft).[35] Category 6a is required to reach the full distance of 100 meters (330 ft) and category 6 may reach a distance of 55 meters (180 ft) depending on the quality of installation, determined only after re-testing to 500 MHz.
1000BASE-T (also called gigabit Ethernet) is the IEEE standard that defines the requirement for sending information at 1000 Mbps on unshielded twisted-pair cabling, and defines various aspects of running baseband Ethernet on this cabling.