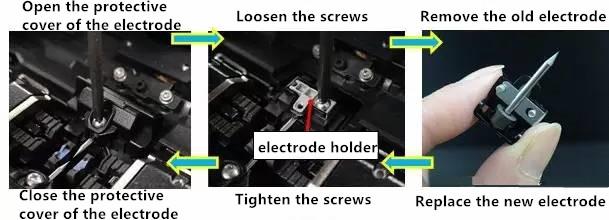
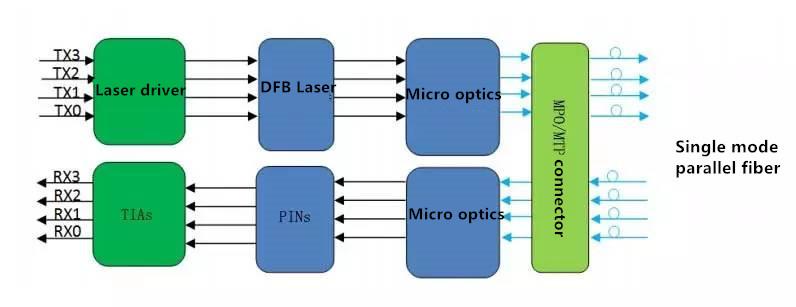
- Related articles
- All Cisco CWDM-GBIC-1570's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility ma
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-58.17's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- All Cisco XFP10GLR192SR-RGD's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- How to Choose an Internal Network Card?
- All Cisco XFP-10GZR-OC192LR’s Information (Overview, Features, Datasheet PDF, Price, Speci
- What Condition is Required to Enable Layer 3 Switching?
- All Cisco DWDM-X2-50.12's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility mat
- What is DWDM in Telecom?
- All Cisco DWDM-XENPAK-60.61's information (List price, Specs, Datasheet PDF, Compatibility
- What is SFP in Networking?

It is hard to imagine computers that were outside of a network due to the rise of the Internet, but there was a time in which computers were loners. Internal network cards allowed computers to become social and communicate with each other. The internal network card has also been known as network interface controllers,, network interface cards (NIC), network adapters,, and in LAN (local area networks) environments, LAN adapter is.
Prior to the mid-1990s, the cards were implemented externally and plugged into the motherboard. Ethernet protocol rose to be the standard, somewhat based on its low cost and versatility. Token rings have all but become obsolete. Each Ethernet card has a unique MAC address, which is a 48-bit serial number that is stored in the ROM (read-only memory). Speeds of Ethernet network cards include support for up to 1000 Megabits per second. The internal network card connects a computer with online services via a modem.
External Network Card

Difference between Internal Network Card and External Network Card
Summary